What is fiber dispersion?How to compensate dispersion?
What is fiber dispersion?
Fiber dispersion shows the propagation state of the input signal in the fiber. It refers to the signal distortion caused by the propagation of different frequency components or different mode components of the optical signal at different speeds.It mainly includes three cases: intermode dispersion, chrominance dispersion and polarization mode dispersion.
Intermodal dispersion
Intermode dispersion is a signal distortion mechanism that occurs in multimode fibers and other waveguides.In a multimode fiber, light rays entering the fiber at different incidence angles are defined as a path or a pattern.As the transmission path of each mode is different, its transmission speed (i.e., group speed) is also different, so there is a time difference between the signal transmission modes to reach the optical fiber terminal.In general, some light passes directly through the core (in axial mode), while others bounce back and forth between cladding/core boundaries and travel zigzag along the waveguide, as shown in the step-index multimode fiber below.The fact is that as soon as light is refracted, intermode/mode dispersion occurs.Among them, the inter-mode dispersion is positively correlated with the transmission path, that is, the inter-mode dispersion caused by the high-order mode (the ray enters at a larger Angle for a longer distance) is higher than that caused by the low-order mode (the ray enters at a smaller Angle for a shorter distance).
1 Intermode dispersion in step-index multimode fibers

Multimode fiber can accommodate up to 17 ray propagation modes at the same time, and its intermode dispersion is much higher than that of single mode fiber.This is because single-mode fibers have a single propagation mode, i.e. light travels along the core (axial mode) without reflecting off the cladding boundary, so no intermode dispersion occurs.However, if a graded index multimode fiber is used, the situation is different.Although light also propagates in different modes, due to the uneven refractive index of the fiber core, the path of light rays is not a straight line but a curve, and the propagation speed of light rays also changes. Therefore, the inter-mode dispersion can be greatly reduced by selecting the appropriate refractive index distribution.
Chroma dispersion
Chrominance dispersion refers to the broadening of optical pulses caused by the different group velocities of different wavelength components in the optical fiber, including material dispersion and waveguide dispersion.

2 Chrominance dispersion
The material dispersion is caused by the dependence of refractive index on the wavelength of the core material, while the waveguide dispersion is caused by the dependence of the mode propagation constant on the fiber parameters (core radius, the difference in refractive index between the core and the cladding) and the signal wavelength.At certain frequencies, material dispersion and waveguide dispersion can cancel each other out, so that a wavelength approximating 0 chroma dispersion is obtained.In fact, chrominance dispersion is not always detrimental.Light travels at different speeds in different wavelengths or materials, causing light pulses to be broadened or compressed in the fiber, which makes it possible to customize refractive index profiles to produce fibers for different purposes.The G.652 optical fiber is one example.
Polarization mode dispersion
Polarization mode dispersion (PMD) reflects the polarization dependence of the propagation characteristics of light waves in optical fibers.In actual optical fibers, there are two polarization modes that are perpendicular to each other. Ideally, the two polarization modes should have the same wave propagation characteristics, but in general, there are subtle differences between different polarization modes.This is due to the change or disturbance of temperature, pressure and other factors in the propagation process, resulting in different transmission speeds of the two polarization modes, resulting in time delay and polarization mode dispersion.

3 Polarization mode dispersion formation
Polarization mode dispersion has little effect on networks with link speeds below 2.5Gbps, even if the transmission distance is greater than 1000 km.However, with the increase of transmission speed, especially when the transmission speed exceeds 10Gbps, the influence of polarization mode dispersion increases dramatically, and becomes a fiber parameter that cannot be ignored.Polarization mode dispersion is mainly produced in the process of glass manufacturing, in addition to the optical fiber wiring, installation and use environment and other factors will affect it.
How to compensate dispersion?
Although fiber dispersion does not weaken the signal, it shortens the propagation distance of the signal inside the fiber and causes signal distortion at the same time.For example, a light pulse of 1 nanosecond at the transmitting end can be broadened to 10 nanoseconds at the receiving end, causing the signal to fail to be received and decoded properly.Therefore, it is very important to reduce fiber dispersion or compensate for it in long distance transmission systems such as dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM).Three commonly used dispersion compensation strategies and methods are introduced below.
Dispersion compensated fiber
Using the technique of dispersion-compensated fiber (DCF), the negative dispersive fiber can be added to the conventional fiber.Compared with the conventional fiber, the dispersion value is very large, and the dispersion is positive, which makes the light distribution in this kind of fiber reduce or even disappear.By adding negative dispersion compensation fiber to it, the total dispersion of the whole fiber line can be approximately zero, so as to realize high speed, large capacity and long distance communication.Dispersion compensation fiber mainly has three compensation mechanisms, including pre compensation, post compensation and symmetry compensation.Dispersion compensation fibers are widely used to upgrade fiber links installed at 1310 nm to operate at 1550 nm.
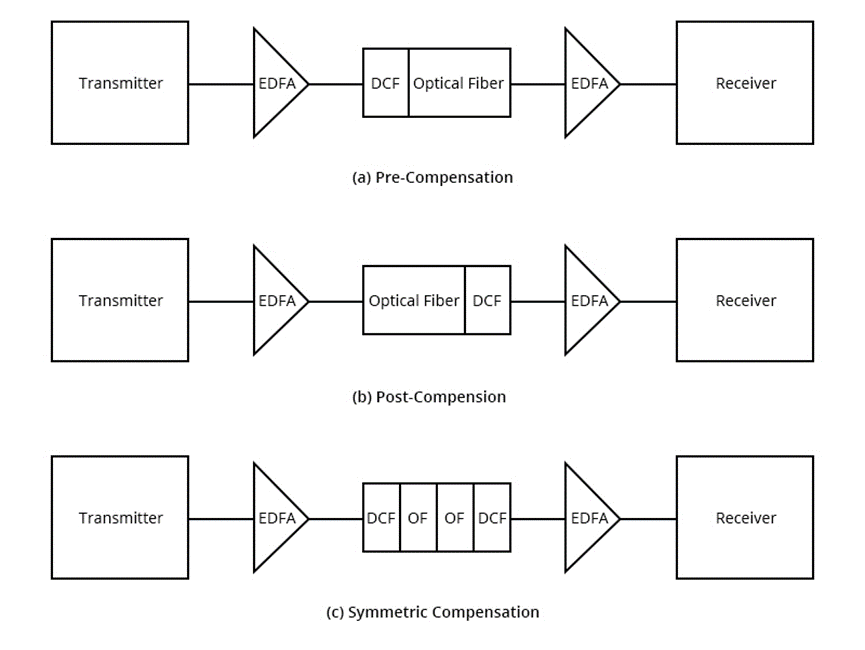
4 Three dispersion compensation mechanisms
Fiber Bragg grating
Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) is a reflection device composed of fiber, which can modulate its core refractive index within a certain range.In long-distance transmission systems such as 100 km, the dispersion effect can be significantly reduced by this device.When the beam passes through the fiber Bragg grating, the wavelength meeting the modulation condition will be reflected, and the rest wavelength will continue to be transmitted along the fiber through the fiber Bragg grating.Using fiber Bragg grating for dispersion compensation has great advantages, because fiber Bragg grating can be integrated with other passive fiber devices, low insertion loss and low cost.In addition, fiber Bragg grating can be used not only as a filter for dispersion compensation, but also as a sensor, a wavelength stabilizer for pumped lasers, and a narrow-band WDM plus/minus filter.
Electron dispersion compensation
Electronic dispersion compensation (EDC) is a method to achieve dispersion compensation in optical communication links using electronic filtering (also known as equalization), that is, filtering in the communication channel to compensate for signal attenuation caused by the transmission medium.The electronic dispersion compensation is usually realized by the transverse filter, whose output is the weighted sum of a series of delayed inputs. It can automatically adjust the filter weight according to the characteristics of the received signal, that is, self-adaptation.Electronic dispersion compensation can be used in single-mode fiber systems and multi-mode fiber systems. In addition, it can be combined with other features for 10Gbit/s receiver integrated circuits.It can significantly reduce the transmitter cost in single-mode fiber systems, and can also increase the transmission distance of multi-mode fiber systems with small receiver cost losses.
Conclusion
Although optical fiber dispersion can affect signal propagation in many ways, and even cause signal distortion, it is not completely unfavorable to signal transmission in optical fiber link.In fact, when wavelength division multiplexing is used, certain optical fiber dispersion can be used to mitigate the nonlinear effect.When the dispersion of the fiber is too large, the above dispersion compensation fiber, fiber Bragg grating, electron dispersion compensation and other methods can be selected for dispersion compensation.

